SWOT analysis: the weak and strong sides of the enterprise in Excel example
The first letters of the English abbreviation SWOT are as follows:
- S – Strengths;
- W – Weaknesses;
- O – Opportunities;
- T – Threats.
The strengths and weaknesses of the enterprise, opportunities and threats from the outside are identified with the help of SWOT analysis. It’s establish the relations between these elements. The components S and W are used to describe the internal environment; O and T are used for describing external ones.
SWOT Analysis Methodology
Analysts can solve a number of problems using this method:
- What internal potentials of the enterprise can become fortes?
- How fully are the existing strengths of the company used?
- Do weaknesses make a company vulnerable?
- Are the weaknesses of the enterprise impeding the full use of favorable circumstances?
- What weaknesses need adjustment?
- What opportunities are open to the firm when accessing certain resources and applying the available qualifications?
With the help of SWOT-analysis the strengths and weaknesses of the enterprise, it's potential and threats are identified and systematized. This is the starting point of any segmentation. In fact, managers compare internal resources and weaknesses with market opportunities. Based on the results of the comparison, the conclusion is drawn: "where does the enterprise need to move on?"
The procedure for conducting the SWOT analysis is as follows:
- Identify strengths and weaknesses.
- Identification of external threats and potentials.
- Establishing the relationship between components.
- Positioning of various ways of further development.
Analyzing an enterprise using the SWOT method is easily and quickly. But this simplicity is also the negative side of this method: the analyst can come to wrong and hasty conclusions.
The external and internal environment of the organization in SWOT analysis
The internal components of the analysis relate directly to the organization of activities in the enterprise. It can be:
- manufacturing process;
- marketing and storage;
- transport and logistic;
- marketing department;
- innovation and technology;
- labor resources;
- security organization;
- material and technical basis, etc.
External elements refer to the environment "surrounding" the enterprise. It can be:
- legislation;
- policy;
- competition;
- socio-demographic situation;
- demand;
- ecological situation in the region, country, world, etc.
SWOT-analysis of the enterprise: strengths and weaknesses
Possible strengths of the company:
- high availability of material resources;
- high professionalism and qualification of the staff;
- established status in the market environment ("name");
- own elaborations and technologies;
- effective advertising campaign;
- low production prime cost;
- financial stability, etc.
Possible weaknesses:
- absence of a forward-looking development plan and clear goals;
- poor working conditions;
- obsolete equipment;
- high prime cost;
- lack of qualified personnel;
- low profitability;
- unsustainable sales channels;
- a narrow range of goods, works and services and so on.
Opportunities and threats
Opportunities are factors that will help an enterprise to develop effectively. For example:
- expansion of the range of goods, works and services;
- entering a new market;
- the forthcoming of investment funds;
- growth in demand for products, etc.
Threats are the circumstances in which the organization may suffer damage. For example:
- unfavorable economic situation in the country;
- increase in the tax burden;
- emergence of a powerful competitor;
- "bad" and unprofitable currencies exchange rates;
- changes in the tastes and preferences of potential customers, etc.
SWOT-analysis of enterprises with an example table in Excel
Sequence of analysis:
- Determination of parameters for the analysis of strengths and weaknesses. You can create a table in the first column of which will be a parameter for the characteristics of the enterprise. In the second will be strengths and in the third will be weaknesses. The company chooses parameters at its discretion:
- The table of threats and opportunities is separately filled out:
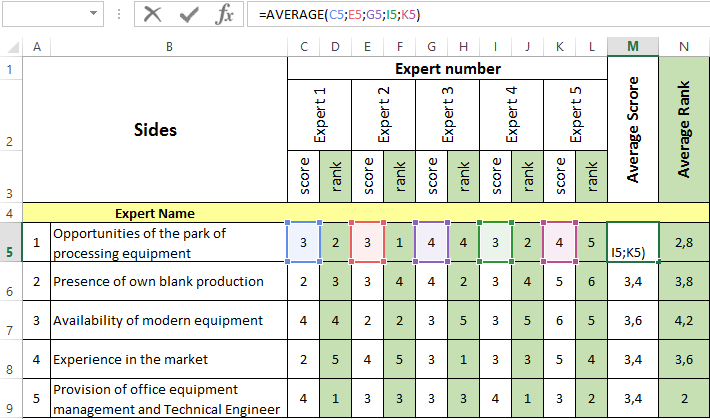
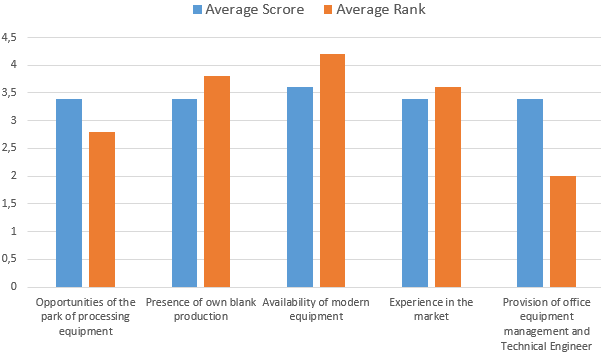
- Then we compile the matrix of factors. An assessment in scores is carried out for impact (for strengths and weaknesses) and probability of use (for opportunities and threats). Several experts should conduct the ranking of factors. For each position put from 1 to 6 points (depending on the degree of influence). Next is the average. Matrix of factors for the analysis of strengths. By the same principle matrixes of factors are formed for the analysis of weaknesses, threats and opportunities.
- You need to select the most significant factors (focusing on points) if too many of them have been identified in the analysis. The best option is up to 5 elements. Optimal is up to 10. Matrixes are used to compose diagrams to make the selection process faster.
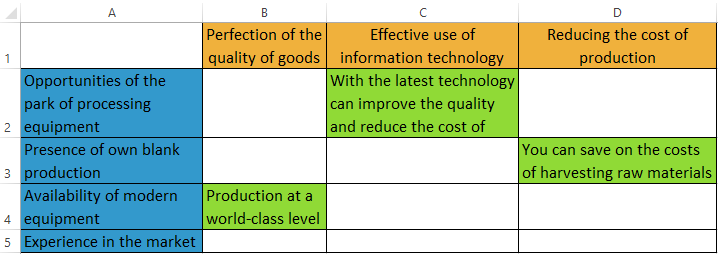
- Then cross tables are compiled in Excel. These are problem fields using which you need to answer a number of questions. What opportunities can a company take advantage of through its strengths? So vertically we make the strengths selected with the help of the matrices. Table head - horizontal - features. In the cell at the intersection is the answer to the question.
| Parameter | Strengths | Weaknesses |
| Production | Professionalism and qualification of personnel | Obsolete equipment |
| The possibility of creating a park of processing equipment | Unbalanced production capacity | |
| Supply | ||
| Innovations | ||
| Financial resources | ||
| Security |
| Parameter | Threat | Opportunity |
| Competition | The implantation of equipment from foreign manufacturers | |
| Economy | ||
| Demand | Dependence of financial condition on the volume of orders from several large buyers | |
| Policy | Effective use of information technology | |
| Socio-demographic situation | ||
| Culture | ||
| Nature and ecology |
Download 15 templates for SWOT analysis
Problem fields are compiled in all areas of analysis:
- How can threats be leveled with strong factors?
- What are the weak aspects of the enterprise impeding in the realization of opportunities?
- What weaknesses further aggravates risks and threats? How?
Answers to questions are written in cells at the intersection of factors.