Trigonometric SIN COS functions in Excel for Sine and Cosine
The SIN function in Excel is used to calculate the sine of an angle given in radians and returns the corresponding value.
The SINH function in Excel returns the value of the hyperbolic sine of a given real number.
The COS function in Excel calculates the cosine of an angle specified in radians and returns the corresponding value.
The COSH function returns the value of the hyperbolic cosine of the given real number.
Examples of using the functions SIN, SINH, COS and COSH in Excel
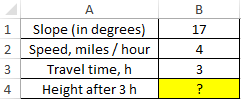
Example 1. A traveler moves up a mountain with a slope of 17°. The speed is constant and is 4 km / h. Determine at what height relative to the starting point of reference it will be after 3 hours.
Data table:
To solve use the formula:
=B2*B3*SIN(RADIANS(B1))
Argument Description:
- B2 * B3 - product of speed and time of a journey, the result of which is the distance traveled (hypotenuse of a right triangle);
- SIN (RADIANS (B1)) is the sine of the gradient expressed in radians using the RADIANS function.
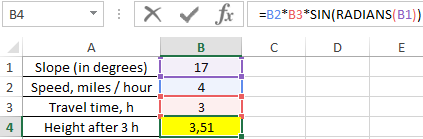
As a result of calculations, we obtained the value of the small leg of a right triangle, which characterizes the height of the traveler.
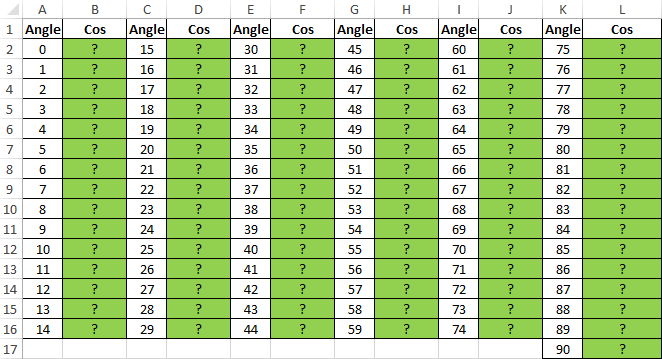
Table of Sines and Cosines in Excel
Example 2. Earlier in educational institutions reference manuals of trigonometric functions were widely used. How can I create my own simple reference book using Excel for cosines of angles from 0 to 90?
Fill the columns with angles in degrees:
To fill, use the COS function as an array formula. An example of filling the first column:
=COS(RADIANS(A2))
Calculate the values for all angles. The result:
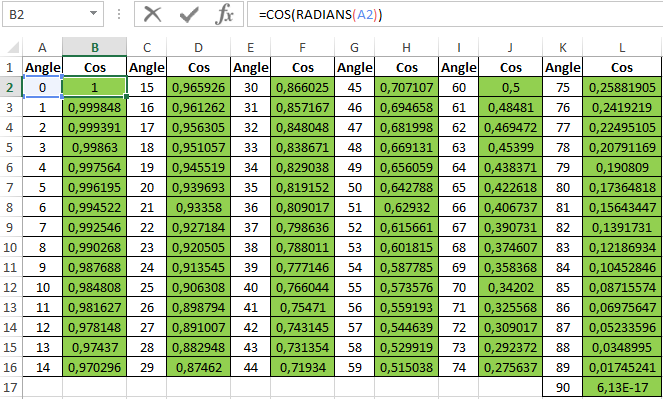
Note: cos (90 °) = 0 is known, but the RADIANS function (90) determines the value of the radians of the angle with a certain error, therefore, a nonzero value was obtained for the 90 ° angle.
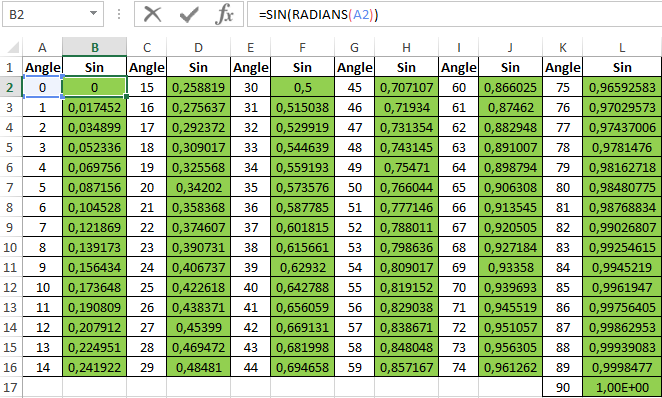
In a similar way, create a sine table in Excel:
Plotting SINH and COSH functions in Excel
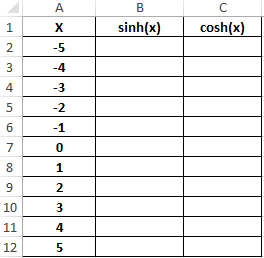
Example 3. Build graphs of the functions sinh (x) and cosh (x) for the same values of the independent variable and compare them.
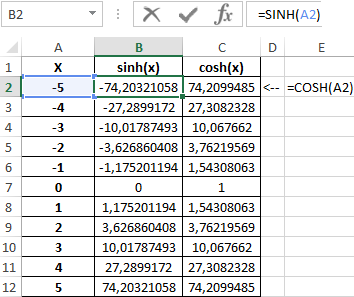
Initial data:
The formula for finding hyperbolic sines:
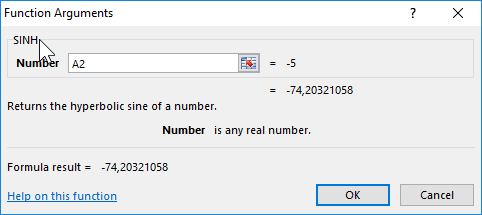
=SINH(A2)
The formula for finding hyperbolic cosines is:
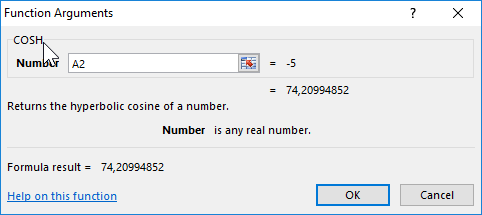
=COSH(A2)
Table of values obtained:
We construct Chart of both functions based on the available data. Select the range of cells A1: C12 and select the tool «INSERT»-«Charts» -«Insert a Scatter (X, Y) or Bubble Chart»-«Scatter with Smooth Lines and Markers»:
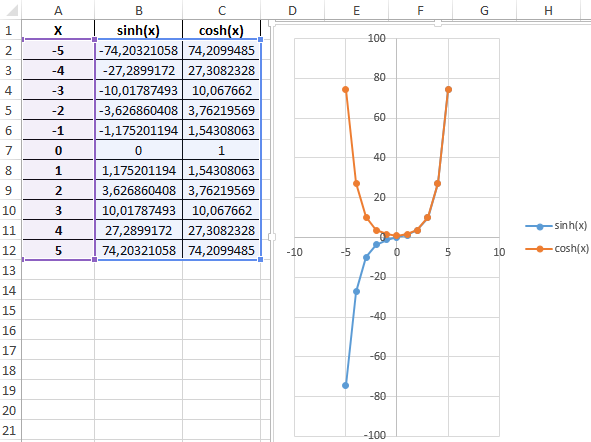
As you can see, the chart coincide on the interval (0; + ∞), and in the area of negative values of X, parts of the graphs are mirror images of each other.
Features of using trigonometric functions in Excel
Syntax of the SIN function:
=SIN( number )
SINH function syntax:
=SINH( number )
COS function syntax:
=COS( number )
COSH function syntax:
>=COSH( number )
Each of the above functions takes a single argument number that characterizes the angle specified in radians (for SIN and COS) or any value from the range of real numbers for which you want to determine the hyperbolic sine or cosine (for SINH and COSH, respectively).
Notes 1:
If, as an argument of any of the functions in question, text data was passed that cannot be converted to a numeric value, the result of the functions will be the error code #VALUE !. For example, the function = SIN (“1”) will return the result 0.8415, because Excel performs data conversion where possible.
As arguments of the functions in question, the logical values TRUE and FALSE can be passed, which will be interpreted as numerical values 1 and 0, respectively.
All considered functions can be used as array formulas.
Notes 2:
- Hyperbolic sine is calculated using the formula: sinh(x)=0,5*(ex-e-x).
- The formula for calculating the hyperbolic cosine is: cosh(x)=0,5*( ex+e-x).
- When calculating the sines and cosines of the angles using the SIN and COS formulas, it is necessary to use radian angle measures. If the angle is specified in degrees, two methods can be used to translate into a radian angle measure:
Download examples trigonometric SIN COS functions in Excel
- The RADIANS function (for example, = SIN(RADIANS(30)) will return the result 0.5;
- The expression PI () * angle_in_gradusah / 180.