Examples of functions for working with dates: YEAR, MONTH and DAY in Excel
Excel spreadsheets provide the ability to work with various types of textual and numerical information. Date processing is also available. In this case, there may be a need to extract from the general meaning of a specific number, for example, a year. There are separate functions for this: YEAR, MONTH, DAY and DAY.
Examples of using functions for date processing in Excel
Excel tables store dates that are presented as a sequence of numeric values. It begins on January 1, 1900. This date will correspond to the number 1. At the same time, January 1, 2009 is laid down in the tables, as the number 39813. This is the number of days between the two designated dates.
The function YEAR is used similarly to the adjacent:
- MONTH;
- DAY;
- WEEKDAY.
All of them display numerical values corresponding to the Gregorian calendar. Even if in the Excel spreadsheet, the Hijra calendar was chosen to display the entered date, then when isolating the year and other composite values by functions, the application will present a number that is equivalent to the Gregorian system of chronology.
To use the YEAR function, you need to enter into the cell the following function formula with one argument:
=YEAR(cell address with date in numeric format)
The function argument is required. It can be replaced by "date_number_number". In the examples below, you can clearly see this. It is important to remember that when displaying the date as text (automatic orientation on the left edge of the cell), the YEAR function will not be executed. Its result will be the # SIGN. Therefore, formatted dates must be presented in a numerical version. Days, months and year can be separated by a dot, slash or comma.
Consider an example of working with the YEAR function in Excel. If we need to get a year from the original date, the function AVAILABLE will not help us since it does not work with dates, but only with text and numeric values. To separate the year, month or day from the full date for this, Excel provides functions for working with dates.
Example: There is a table with a list of dates and in each of them it is necessary to separate the value of only the year.
We introduce the original data in Excel.
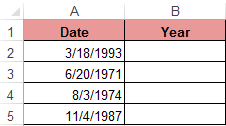
To solve the problem, it is necessary to enter the formula in the cells of column B:
=YEAR(the address of the cell, from the date of which you need to isolate the year value)
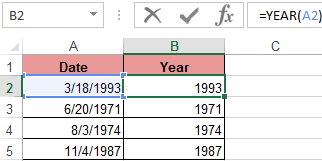
As a result, we extract years from each date.
A similar example of the MONTH function in Excel:
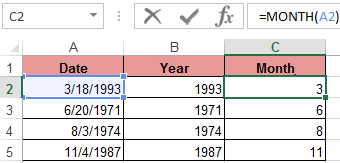
An example of working with functions DAY and WEEKDAY. The DAY function gets to calculate from the date the number of any day:
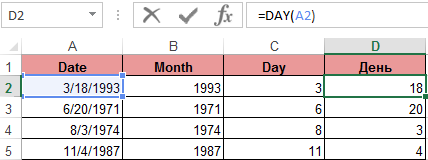
WEEKDAY function returns the number of the day of the week (1-Monday, 2-Tuesday ..., etc.) for any date:
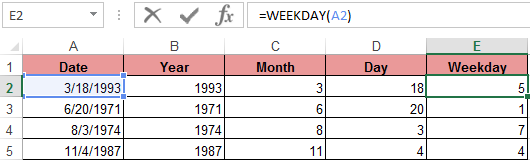
In the second optional argument of the WEEKDAY function, the number 2 may specified for our day of the week countdown format (Monday-1 through Sunday-7):
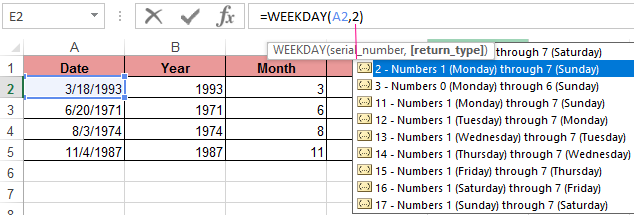
If you omit the second optional argument, then the default format will be used (English from Sunday-1 to Saturday-7).
Create a formula of the combination of the functions INDEX and WEEKDAY:
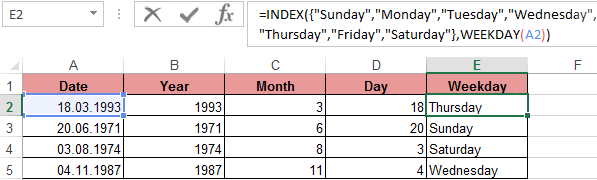
We obtain a more understandable form of the implementation of this function.
Examples of the practical use of functions for working with dates
These primitive functions are very useful when grouping data by: years, months, days of the week, and specific days.
Suppose we have a simple sales report:
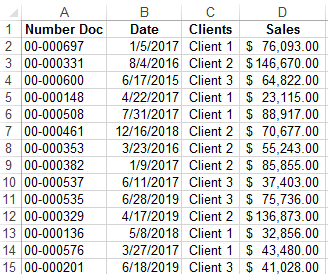
We need to quickly organize data for visual analysis without using pivot tables. To do this, we will bring the report into a table where it is convenient and quickly to group data by year, month and day of the week:
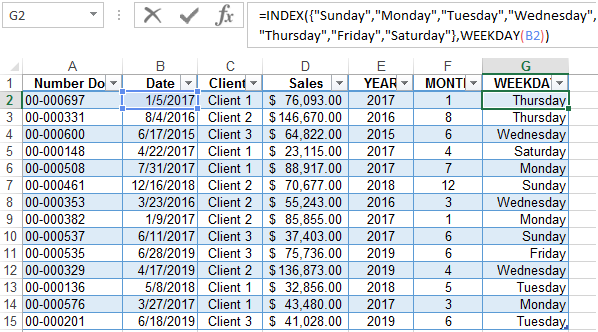
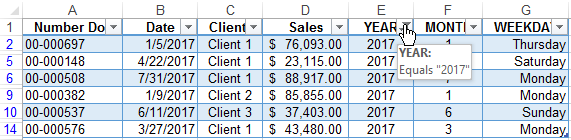
Now we have a tool to work with this sales report. We can filter and segment data by specific time criteria:
In addition, you can make a histogram to analyze the best-selling days of the week, to understand which day of the week has the largest number of sales:
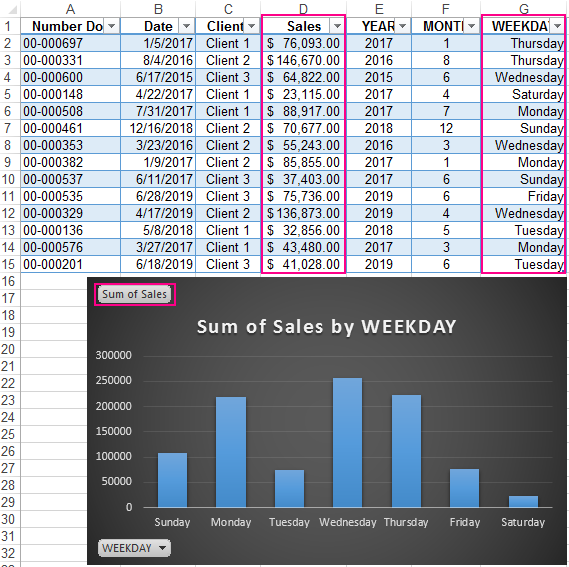
In this form, it is very convenient to segment sales reports for long, medium and short periods of time.
It should be immediately noted that in order to get the difference between the two dates, none of the above functions will help us. For this task, you should use a specially designed function DATEDIF:
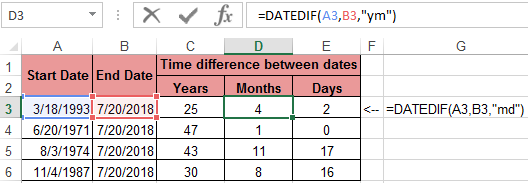
Download examples fo functions YEAR MONTH DAY WEEKDAY and DATEDIF
The type of values in the date cells requires a special approach to data processing. Therefore, you should use the appropriate type of function in Excel.